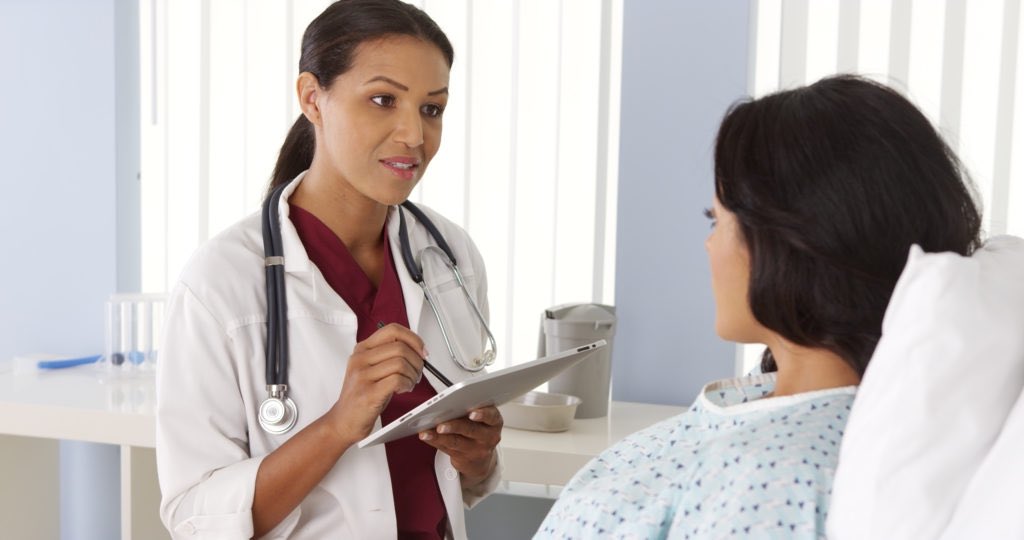
A colonoscopy is an exam used to look inside the large intestine (or colon) and rectum. A colonoscopy allows doctors to detect changes or abnormalities in the GI tract that could be signs of cancer. This exam can also be used to diagnose reasons for pain, weight loss, or a change in bowel movements. During the procedure, a flexible, long tube called a colonoscope is inserted into the rectum. The colonoscope has a tiny video camera and light attached to the tip of the tube. Doctors use the video camera to see the inside of the colon. They may take tissue samples for biopsy or remove polyps during the exam. Colonoscopies are outpatient procedures usually performed by gastroenterologists.
Patients are sedated and won’t feel anything during the procedure. Barring complications, which are very rare, the procedure lasts about an hour. Doctors recommend colonoscopies for patients who are age 50 or older and who are at average risk for colon cancer. After the colonoscopy, patients spend 30 minutes in recovery, until the sedative wears off. Patients may not drive immediately after the procedure, so it’s a good idea to bring someone with you.
Are there alternatives to a colonoscopy?
If your doctor tells you that you need a colonoscopy, it’s usually because you’ve tried other options without success. Colonoscopies are a valuable tool to prevent colorectal health issues, but there are other options to screen for colon cancer. Talk with your doctor to find out if any of these options are right for you.
- CT colonography (virtual colonoscopy) – A computed tomography (CT) colonography, also called a virtual colonoscopy, uses X-rays and computers to generate 3-D pictures of the colon. The images are displayed on a computer screen for the doctor to review.
- Flexible sigmoidoscopy – A flexible sigmoidoscopy is a procedure similar to a colonoscopy. A medical professional uses a long, flexible tube with a light and camera on one end, called a sigmoidoscope or scope, to look into the rectum and lower colon. This procedure may not require anesthesia.
- Stool tests – Several stool tests are available for at-home colon cancer testing. The guaiac-based fecal occult blood test (gFOBT) uses a chemical to detect blood in the stool. The fecal immunochemical test (FIT) uses antibodies to test for blood in the stool. The FIT-DNA test, also called the DNA test, detects DNA in the stool and requires an entire bowel movement to be sent to a lab.
The type of procedure you get will depend on your personal health and your doctor’s recommendations. You can always ask your doctor why they’re recommending any procedure. If you’re unsure about their recommendations, feel free to get a second opinion.
How much should you pay for your colonoscopy?
Many patients don’t realize that they have the right to shop around for the best value for their medical procedures. If your doctor has recommended a colonoscopy, there are choices that you can make that will help you pay less for your test. Visit New Choice Health’s colonoscopy cost page to learn more about how much you should expect to pay for your colonoscopy, as well as what factors may affect the cost of your medical procedure.